nnUNet是一个自适应的深度学习框架,专为医学图像分割任务设计。以下是关于nnUNet的详细解释和特点:
自适应框架:nnUNet能够根据具体的医学图像分割任务自动调整模型结构、训练参数等,从而避免了繁琐的手工调参过程。
自动化流程:nnUNet包含了从数据预处理到模型训练、验证及测试的全流程自动化工具,大大简化了使用深度学习进行医学图像分割的复杂度。
自适应网络结构调整:根据输入数据集的特点,nnUNet能够自动选择和配置合适的网络深度、宽度等超参数,确保模型在复杂性和性能之间取得平衡。
Patch-Based Training and Inference:nnUNet使用基于patch级别的训练方法,通过滑窗的方式遍历整个图像进行训练。在推理阶段,也采用类似的方法来生成整个图像的分割结果。这种方法对于处理大尺寸图像或有限显存的情况非常有效。
集成学习与交叉验证:nnUNet还采用了交叉验证策略以最大程度利用有限的数据集,并结合集成学习技术来提高模型预测的稳定性和准确性。
此外,nnUNet还提供了丰富的文档和示例,帮助用户更好地了解和使用该框架。要使用nnUNet,用户需要安装Python和相应的深度学习框架,然后按照官方文档提供的步骤进行操作即可。总的来说,nnUNet是一个功能强大、易于使用的深度学习框架,特别适用于医学图像分割任务。它的自适应特性、自动化流程和先进的训练策略使得用户能够更高效地构建和训练模型,同时获得更好的性能表现。
之前已经介绍过nnunet的安装、使用以及自定义网络的教程,本文介绍在nnunet中加入ChannelAttention的方法,阅读本文前,请确保已经掌握以下内容:
【nnUNetv2实践】一、nnUNetv2安装
【nnUNetv2实践】二、nnUNetv2快速入门-训练验证推理集成一条龙教程
【nnUNetv2进阶】三、nnUNetv2 自定义网络-发paper必会-CSDN博客

本文介绍在nnunet中加入ChannelAttention的方法,ChannelAttention是一种非常简单的注意力机制,非常适合魔改网络练手之用,更高级的魔改教程后续慢慢推出。
一、ChannelAttention
ChannelAttention就是通道注意力机制,其2D代码非常简单,这里不过多介绍其原理,各位朋友可自行搜索其原理。
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels: int) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
self.act = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return x * self.act(self.fc(self.pool(x)))二、nnunet加入ChannelAttention
之前的教程已经提到过,nnunet的网络需要在dynamic-network-architectures中修改,并在数据集的plan中修改来实现自己的网络训练。
1、网络结构修改
在dynamic-network-architectures的architectures目录下新建caunet.py:
caunet的代码如下所示:
from typing import Union, Type, List, Tuple
import torch
from dynamic_network_architectures.building_blocks.helper import convert_conv_op_to_dim
from dynamic_network_architectures.initialization.weight_init import InitWeights_He
from torch import nn
from torch.nn.modules.conv import _ConvNd
from torch.nn.modules.dropout import _DropoutNd
from dynamic_network_architectures.building_blocks.helper import maybe_convert_scalar_to_list, get_matching_pool_op
import numpy as np
from dynamic_network_architectures.building_blocks.helper import get_matching_convtransp
class CAPlainConvUNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
input_channels: int,
n_stages: int,
features_per_stage: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
conv_op: Type[_ConvNd],
kernel_sizes: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
strides: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
n_conv_per_stage: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
num_classes: int,
n_conv_per_stage_decoder: Union[int, Tuple[int, ...], List[int]],
conv_bias: bool = False,
norm_op: Union[None, Type[nn.Module]] = None,
norm_op_kwargs: dict = None,
dropout_op: Union[None, Type[_DropoutNd]] = None,
dropout_op_kwargs: dict = None,
nonlin: Union[None, Type[torch.nn.Module]] = None,
nonlin_kwargs: dict = None,
deep_supervision: bool = False,
nonlin_first: bool = False
):
"""
nonlin_first: if True you get conv -> nonlin -> norm. Else it's conv -> norm -> nonlin
"""
super().__init__()
if isinstance(n_conv_per_stage, int):
n_conv_per_stage = [n_conv_per_stage] * n_stages
if isinstance(n_conv_per_stage_decoder, int):
n_conv_per_stage_decoder = [n_conv_per_stage_decoder] * (n_stages - 1)
assert len(n_conv_per_stage) == n_stages, "n_conv_per_stage must have as many entries as we have " \
f"resolution stages. here: {n_stages}. " \
f"n_conv_per_stage: {n_conv_per_stage}"
assert len(n_conv_per_stage_decoder) == (n_stages - 1), "n_conv_per_stage_decoder must have one less entries " \
f"as we have resolution stages. here: {n_stages} " \
f"stages, so it should have {n_stages - 1} entries. " \
f"n_conv_per_stage_decoder: {n_conv_per_stage_decoder}"
self.encoder = CAPlainConvEncoder(input_channels, n_stages, features_per_stage, conv_op, kernel_sizes, strides,
n_conv_per_stage, conv_bias, norm_op, norm_op_kwargs, dropout_op,
dropout_op_kwargs, nonlin, nonlin_kwargs, return_skips=True,
nonlin_first=nonlin_first)
self.decoder = CAUNetDecoder(self.encoder, num_classes, n_conv_per_stage_decoder, deep_supervision,
nonlin_first=nonlin_first)
print('using ca unet...')
def forward(self, x):
skips = self.encoder(x)
return self.decoder(skips)
def compute_conv_feature_map_size(self, input_size):
assert len(input_size) == convert_conv_op_to_dim(self.encoder.conv_op), "just give the image size without color/feature channels or " \
"batch channel. Do not give input_size=(b, c, x, y(, z)). " \
"Give input_size=(x, y(, z))!"
return self.encoder.compute_conv_feature_map_size(input_size) + self.decoder.compute_conv_feature_map_size(input_size)
@staticmethod
def initialize(module):
InitWeights_He(1e-2)(module)
class CAPlainConvEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
input_channels: int,
n_stages: int,
features_per_stage: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
conv_op: Type[_ConvNd],
kernel_sizes: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
strides: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
n_conv_per_stage: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
conv_bias: bool = False,
norm_op: Union[None, Type[nn.Module]] = None,
norm_op_kwargs: dict = None,
dropout_op: Union[None, Type[_DropoutNd]] = None,
dropout_op_kwargs: dict = None,
nonlin: Union[None, Type[torch.nn.Module]] = None,
nonlin_kwargs: dict = None,
return_skips: bool = False,
nonlin_first: bool = False,
pool: str = 'conv'
):
super().__init__()
if isinstance(kernel_sizes, int):
kernel_sizes = [kernel_sizes] * n_stages
if isinstance(features_per_stage, int):
features_per_stage = [features_per_stage] * n_stages
if isinstance(n_conv_per_stage, int):
n_conv_per_stage = [n_conv_per_stage] * n_stages
if isinstance(strides, int):
strides = [strides] * n_stages
assert len(kernel_sizes) == n_stages, "kernel_sizes must have as many entries as we have resolution stages (n_stages)"
assert len(n_conv_per_stage) == n_stages, "n_conv_per_stage must have as many entries as we have resolution stages (n_stages)"
assert len(features_per_stage) == n_stages, "features_per_stage must have as many entries as we have resolution stages (n_stages)"
assert len(strides) == n_stages, "strides must have as many entries as we have resolution stages (n_stages). " \
"Important: first entry is recommended to be 1, else we run strided conv drectly on the input"
stages = []
for s in range(n_stages):
stage_modules = []
if pool == 'max' or pool == 'avg':
if (isinstance(strides[s], int) and strides[s] != 1) or \
isinstance(strides[s], (tuple, list)) and any([i != 1 for i in strides[s]]):
stage_modules.append(get_matching_pool_op(conv_op, pool_type=pool)(kernel_size=strides[s], stride=strides[s]))
conv_stride = 1
elif pool == 'conv':
conv_stride = strides[s]
else:
raise RuntimeError()
stage_modules.append(CAStackedConvBlocks(
n_conv_per_stage[s], conv_op, input_channels, features_per_stage[s], kernel_sizes[s], conv_stride,
conv_bias, norm_op, norm_op_kwargs, dropout_op, dropout_op_kwargs, nonlin, nonlin_kwargs, nonlin_first
))
stages.append(nn.Sequential(*stage_modules))
input_channels = features_per_stage[s]
self.stages = nn.Sequential(*stages)
self.output_channels = features_per_stage
self.strides = [maybe_convert_scalar_to_list(conv_op, i) for i in strides]
self.return_skips = return_skips
# we store some things that a potential decoder needs
self.conv_op = conv_op
self.norm_op = norm_op
self.norm_op_kwargs = norm_op_kwargs
self.nonlin = nonlin
self.nonlin_kwargs = nonlin_kwargs
self.dropout_op = dropout_op
self.dropout_op_kwargs = dropout_op_kwargs
self.conv_bias = conv_bias
self.kernel_sizes = kernel_sizes
def forward(self, x):
ret = []
for s in self.stages:
x = s(x)
ret.append(x)
if self.return_skips:
return ret
else:
return ret[-1]
def compute_conv_feature_map_size(self, input_size):
output = np.int64(0)
for s in range(len(self.stages)):
if isinstance(self.stages[s], nn.Sequential):
for sq in self.stages[s]:
if hasattr(sq, 'compute_conv_feature_map_size'):
output += self.stages[s][-1].compute_conv_feature_map_size(input_size)
else:
output += self.stages[s].compute_conv_feature_map_size(input_size)
input_size = [i // j for i, j in zip(input_size, self.strides[s])]
return output
class CAUNetDecoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
encoder: Union[CAPlainConvEncoder],
num_classes: int,
n_conv_per_stage: Union[int, Tuple[int, ...], List[int]],
deep_supervision,
nonlin_first: bool = False,
norm_op: Union[None, Type[nn.Module]] = None,
norm_op_kwargs: dict = None,
dropout_op: Union[None, Type[_DropoutNd]] = None,
dropout_op_kwargs: dict = None,
nonlin: Union[None, Type[torch.nn.Module]] = None,
nonlin_kwargs: dict = None,
conv_bias: bool = None
):
"""
This class needs the skips of the encoder as input in its forward.
the encoder goes all the way to the bottleneck, so that's where the decoder picks up. stages in the decoder
are sorted by order of computation, so the first stage has the lowest resolution and takes the bottleneck
features and the lowest skip as inputs
the decoder has two (three) parts in each stage:
1) conv transpose to upsample the feature maps of the stage below it (or the bottleneck in case of the first stage)
2) n_conv_per_stage conv blocks to let the two inputs get to know each other and merge
3) (optional if deep_supervision=True) a segmentation output Todo: enable upsample logits?
:param encoder:
:param num_classes:
:param n_conv_per_stage:
:param deep_supervision:
"""
super().__init__()
self.deep_supervision = deep_supervision
self.encoder = encoder
self.num_classes = num_classes
n_stages_encoder = len(encoder.output_channels)
if isinstance(n_conv_per_stage, int):
n_conv_per_stage = [n_conv_per_stage] * (n_stages_encoder - 1)
assert len(n_conv_per_stage) == n_stages_encoder - 1, "n_conv_per_stage must have as many entries as we have " \
"resolution stages - 1 (n_stages in encoder - 1), " \
"here: %d" % n_stages_encoder
transpconv_op = get_matching_convtransp(conv_op=encoder.conv_op)
conv_bias = encoder.conv_bias if conv_bias is None else conv_bias
norm_op = encoder.norm_op if norm_op is None else norm_op
norm_op_kwargs = encoder.norm_op_kwargs if norm_op_kwargs is None else norm_op_kwargs
dropout_op = encoder.dropout_op if dropout_op is None else dropout_op
dropout_op_kwargs = encoder.dropout_op_kwargs if dropout_op_kwargs is None else dropout_op_kwargs
nonlin = encoder.nonlin if nonlin is None else nonlin
nonlin_kwargs = encoder.nonlin_kwargs if nonlin_kwargs is None else nonlin_kwargs
# we start with the bottleneck and work out way up
stages = []
transpconvs = []
seg_layers = []
for s in range(1, n_stages_encoder):
input_features_below = encoder.output_channels[-s]
input_features_skip = encoder.output_channels[-(s + 1)]
stride_for_transpconv = encoder.strides[-s]
transpconvs.append(transpconv_op(
input_features_below, input_features_skip, stride_for_transpconv, stride_for_transpconv,
bias=conv_bias
))
# input features to conv is 2x input_features_skip (concat input_features_skip with transpconv output)
stages.append(CAStackedConvBlocks(
n_conv_per_stage[s-1], encoder.conv_op, 2 * input_features_skip, input_features_skip,
encoder.kernel_sizes[-(s + 1)], 1,
conv_bias,
norm_op,
norm_op_kwargs,
dropout_op,
dropout_op_kwargs,
nonlin,
nonlin_kwargs,
nonlin_first
))
# we always build the deep supervision outputs so that we can always load parameters. If we don't do this
# then a model trained with deep_supervision=True could not easily be loaded at inference time where
# deep supervision is not needed. It's just a convenience thing
seg_layers.append(encoder.conv_op(input_features_skip, num_classes, 1, 1, 0, bias=True))
self.stages = nn.ModuleList(stages)
self.transpconvs = nn.ModuleList(transpconvs)
self.seg_layers = nn.ModuleList(seg_layers)
def forward(self, skips):
"""
we expect to get the skips in the order they were computed, so the bottleneck should be the last entry
:param skips:
:return:
"""
lres_input = skips[-1]
seg_outputs = []
for s in range(len(self.stages)):
x = self.transpconvs[s](lres_input)
x = torch.cat((x, skips[-(s+2)]), 1)
x = self.stages[s](x)
if self.deep_supervision:
seg_outputs.append(self.seg_layers[s](x))
elif s == (len(self.stages) - 1):
seg_outputs.append(self.seg_layers[-1](x))
lres_input = x
# invert seg outputs so that the largest segmentation prediction is returned first
seg_outputs = seg_outputs[::-1]
if not self.deep_supervision:
r = seg_outputs[0]
else:
r = seg_outputs
return r
def compute_conv_feature_map_size(self, input_size):
"""
IMPORTANT: input_size is the input_size of the encoder!
:param input_size:
:return:
"""
# first we need to compute the skip sizes. Skip bottleneck because all output feature maps of our ops will at
# least have the size of the skip above that (therefore -1)
skip_sizes = []
for s in range(len(self.encoder.strides) - 1):
skip_sizes.append([i // j for i, j in zip(input_size, self.encoder.strides[s])])
input_size = skip_sizes[-1]
# print(skip_sizes)
assert len(skip_sizes) == len(self.stages)
# our ops are the other way around, so let's match things up
output = np.int64(0)
for s in range(len(self.stages)):
# print(skip_sizes[-(s+1)], self.encoder.output_channels[-(s+2)])
# conv blocks
output += self.stages[s].compute_conv_feature_map_size(skip_sizes[-(s+1)])
# trans conv
output += np.prod([self.encoder.output_channels[-(s+2)], *skip_sizes[-(s+1)]], dtype=np.int64)
# segmentation
if self.deep_supervision or (s == (len(self.stages) - 1)):
output += np.prod([self.num_classes, *skip_sizes[-(s+1)]], dtype=np.int64)
return output
class CAStackedConvBlocks(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
num_convs: int,
conv_op: Type[_ConvNd],
input_channels: int,
output_channels: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
kernel_size: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
initial_stride: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
conv_bias: bool = False,
norm_op: Union[None, Type[nn.Module]] = None,
norm_op_kwargs: dict = None,
dropout_op: Union[None, Type[_DropoutNd]] = None,
dropout_op_kwargs: dict = None,
nonlin: Union[None, Type[torch.nn.Module]] = None,
nonlin_kwargs: dict = None,
nonlin_first: bool = False
):
"""
:param conv_op:
:param num_convs:
:param input_channels:
:param output_channels: can be int or a list/tuple of int. If list/tuple are provided, each entry is for
one conv. The length of the list/tuple must then naturally be num_convs
:param kernel_size:
:param initial_stride:
:param conv_bias:
:param norm_op:
:param norm_op_kwargs:
:param dropout_op:
:param dropout_op_kwargs:
:param nonlin:
:param nonlin_kwargs:
"""
super().__init__()
if not isinstance(output_channels, (tuple, list)):
output_channels = [output_channels] * num_convs
self.convs = nn.Sequential(
ConvDropoutNormReLU(
conv_op, input_channels, output_channels[0], kernel_size, initial_stride, conv_bias, norm_op,
norm_op_kwargs, dropout_op, dropout_op_kwargs, nonlin, nonlin_kwargs, nonlin_first
),
*[
ConvDropoutNormReLU(
conv_op, output_channels[i - 1], output_channels[i], kernel_size, 1, conv_bias, norm_op,
norm_op_kwargs, dropout_op, dropout_op_kwargs, nonlin, nonlin_kwargs, nonlin_first
)
for i in range(1, num_convs-1)
],
CA(
conv_op, output_channels[-2], output_channels[-1], kernel_size, 1, conv_bias, norm_op,
norm_op_kwargs, dropout_op, dropout_op_kwargs, nonlin, nonlin_kwargs, nonlin_first
)
)
self.act = nonlin(**nonlin_kwargs)
self.output_channels = output_channels[-1]
self.initial_stride = maybe_convert_scalar_to_list(conv_op, initial_stride)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.convs(x)
out = self.act(out)
return out
def compute_conv_feature_map_size(self, input_size):
assert len(input_size) == len(self.initial_stride), "just give the image size without color/feature channels or " \
"batch channel. Do not give input_size=(b, c, x, y(, z)). " \
"Give input_size=(x, y(, z))!"
output = self.convs[0].compute_conv_feature_map_size(input_size)
size_after_stride = [i // j for i, j in zip(input_size, self.initial_stride)]
for b in self.convs[1:]:
output += b.compute_conv_feature_map_size(size_after_stride)
return output
class ConvDropoutNormReLU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
conv_op: Type[_ConvNd],
input_channels: int,
output_channels: int,
kernel_size: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
stride: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
conv_bias: bool = False,
norm_op: Union[None, Type[nn.Module]] = None,
norm_op_kwargs: dict = None,
dropout_op: Union[None, Type[_DropoutNd]] = None,
dropout_op_kwargs: dict = None,
nonlin: Union[None, Type[torch.nn.Module]] = None,
nonlin_kwargs: dict = None,
nonlin_first: bool = False
):
super(ConvDropoutNormReLU, self).__init__()
self.input_channels = input_channels
self.output_channels = output_channels
stride = maybe_convert_scalar_to_list(conv_op, stride)
self.stride = stride
kernel_size = maybe_convert_scalar_to_list(conv_op, kernel_size)
if norm_op_kwargs is None:
norm_op_kwargs = {}
if nonlin_kwargs is None:
nonlin_kwargs = {}
ops = []
self.conv = conv_op(
input_channels,
output_channels,
kernel_size,
stride,
padding=[(i - 1) // 2 for i in kernel_size],
dilation=1,
bias=conv_bias,
)
ops.append(self.conv)
if dropout_op is not None:
self.dropout = dropout_op(**dropout_op_kwargs)
ops.append(self.dropout)
if norm_op is not None:
self.norm = norm_op(output_channels, **norm_op_kwargs)
ops.append(self.norm)
if nonlin is not None:
self.nonlin = nonlin(**nonlin_kwargs)
ops.append(self.nonlin)
if nonlin_first and (norm_op is not None and nonlin is not None):
ops[-1], ops[-2] = ops[-2], ops[-1]
self.all_modules = nn.Sequential(*ops)
def forward(self, x):
return self.all_modules(x)
def compute_conv_feature_map_size(self, input_size):
assert len(input_size) == len(self.stride), "just give the image size without color/feature channels or " \
"batch channel. Do not give input_size=(b, c, x, y(, z)). " \
"Give input_size=(x, y(, z))!"
output_size = [i // j for i, j in zip(input_size, self.stride)] # we always do same padding
return np.prod([self.output_channels, *output_size], dtype=np.int64)
class ConvDropoutNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
conv_op: Type[_ConvNd],
input_channels: int,
output_channels: int,
kernel_size: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
stride: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
conv_bias: bool = False,
norm_op: Union[None, Type[nn.Module]] = None,
norm_op_kwargs: dict = None,
dropout_op: Union[None, Type[_DropoutNd]] = None,
dropout_op_kwargs: dict = None,
nonlin: Union[None, Type[torch.nn.Module]] = None,
nonlin_kwargs: dict = None,
nonlin_first: bool = False
):
super(ConvDropoutNorm, self).__init__()
self.input_channels = input_channels
self.output_channels = output_channels
stride = maybe_convert_scalar_to_list(conv_op, stride)
self.stride = stride
kernel_size = maybe_convert_scalar_to_list(conv_op, kernel_size)
if norm_op_kwargs is None:
norm_op_kwargs = {}
if nonlin_kwargs is None:
nonlin_kwargs = {}
ops = []
self.conv = conv_op(
input_channels,
output_channels,
kernel_size,
stride,
padding=[(i - 1) // 2 for i in kernel_size],
dilation=1,
bias=conv_bias,
)
ops.append(self.conv)
if dropout_op is not None:
self.dropout = dropout_op(**dropout_op_kwargs)
ops.append(self.dropout)
if norm_op is not None:
self.norm = norm_op(output_channels, **norm_op_kwargs)
ops.append(self.norm)
self.all_modules = nn.Sequential(*ops)
def forward(self, x):
return self.all_modules(x)
def compute_conv_feature_map_size(self, input_size):
assert len(input_size) == len(self.stride), "just give the image size without color/feature channels or " \
"batch channel. Do not give input_size=(b, c, x, y(, z)). " \
"Give input_size=(x, y(, z))!"
output_size = [i // j for i, j in zip(input_size, self.stride)] # we always do same padding
return np.prod([self.output_channels, *output_size], dtype=np.int64)
class CA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
conv_op: Type[_ConvNd],
input_channels: int,
output_channels: int,
kernel_size: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
stride: Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, ...]],
conv_bias: bool = False,
norm_op: Union[None, Type[nn.Module]] = None,
norm_op_kwargs: dict = None,
dropout_op: Union[None, Type[_DropoutNd]] = None,
dropout_op_kwargs: dict = None,
nonlin: Union[None, Type[torch.nn.Module]] = None,
nonlin_kwargs: dict = None,
nonlin_first: bool = False
):
super(CA, self).__init__()
self.input_channels = input_channels
self.output_channels = output_channels
stride = maybe_convert_scalar_to_list(conv_op, stride)
self.stride = stride
kernel_size = maybe_convert_scalar_to_list(conv_op, kernel_size)
if norm_op_kwargs is None:
norm_op_kwargs = {}
if nonlin_kwargs is None:
nonlin_kwargs = {}
ops = []
self.conv = conv_op(
input_channels,
output_channels,
kernel_size,
stride,
padding=[(i - 1) // 2 for i in kernel_size],
dilation=1,
bias=conv_bias,
)
ops.append(self.conv)
if dropout_op is not None:
self.dropout = dropout_op(**dropout_op_kwargs)
ops.append(self.dropout)
if norm_op is not None:
self.norm = norm_op(output_channels, **norm_op_kwargs)
ops.append(self.norm)
self.all_modules = nn.Sequential(*ops)
self.ca = ChannelAttention(conv_op=conv_op, channels=output_channels)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.all_modules(x)
x = self.ca(x) * x
# x = self.sa(x) * x
return x
def compute_conv_feature_map_size(self, input_size):
assert len(input_size) == len(self.stride), "just give the image size without color/feature channels or " \
"batch channel. Do not give input_size=(b, c, x, y(, z)). " \
"Give input_size=(x, y(, z))!"
output_size = [i // j for i, j in zip(input_size, self.stride)] # we always do same padding
return np.prod([self.output_channels, *output_size], dtype=np.int64)
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
"""Channel-attention module https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/tree/v3.0.0rc1/configs/rtmdet."""
def __init__(self, conv_op, channels: int) -> None:
"""Initializes the class and sets the basic configurations and instance variables required."""
super().__init__()
if conv_op == torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d:
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
elif conv_op == torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv3d:
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool3d(1)
self.fc = nn.Conv3d(channels, channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
self.act = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Applies forward pass using activation on convolutions of the input, optionally using batch normalization."""
return x * self.act(self.fc(self.pool(x)))
简单说下修改思路:在plainconvunet的StackedConvBlocks中加入ChannelAttention模块。
2、配置文件修改
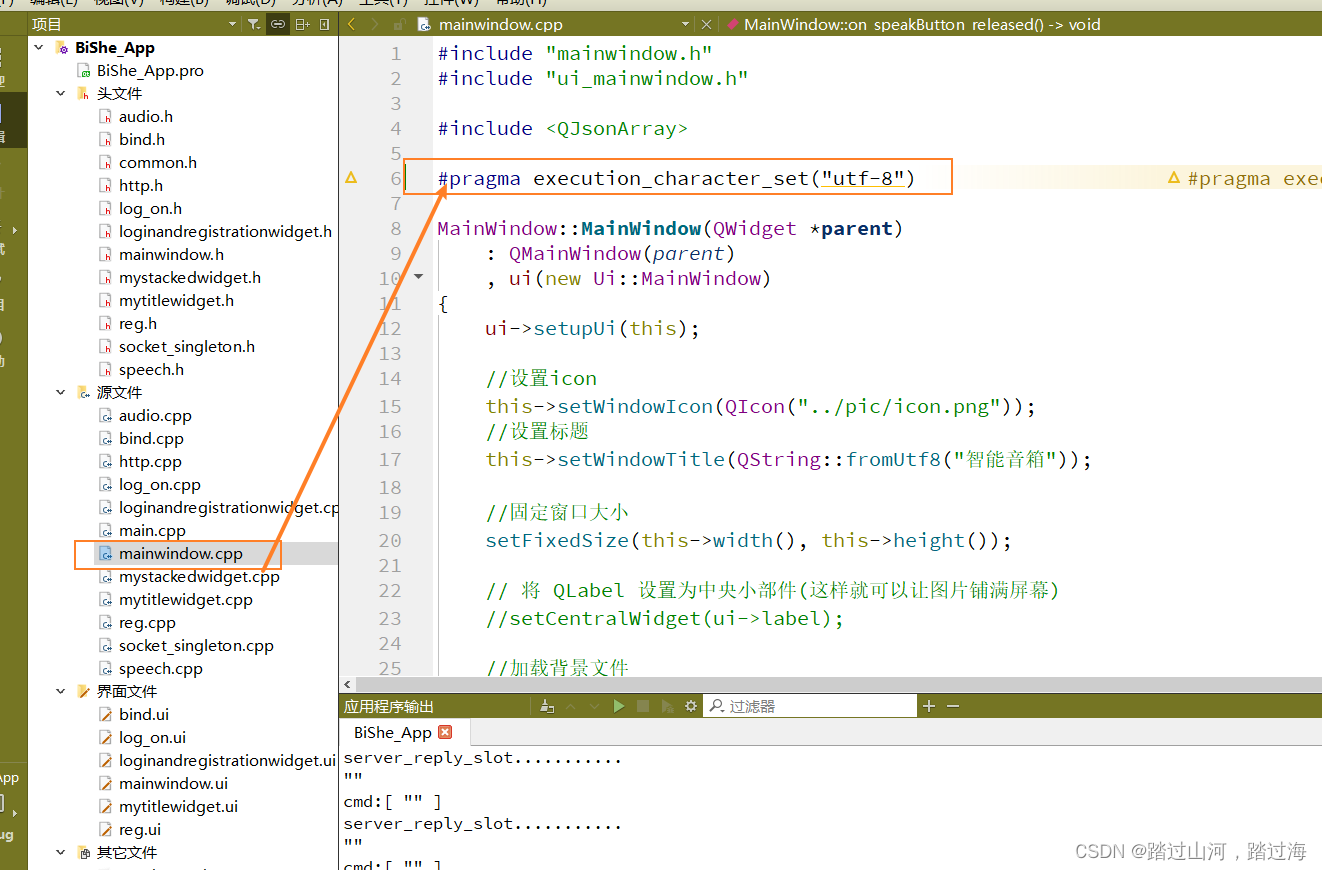
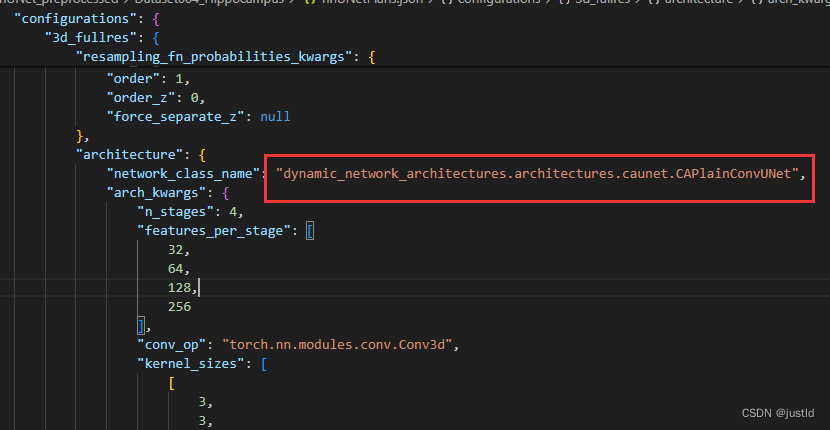
在完成了模型修改后,还是用上个教程的Task04_Hippocampus数据集来验证(如果没做上个教程的,自行完成数据处理),编辑nnUNet\nnUNet_preprocessed\Dataset004_Hippocampus\nnUNetPlans.json这个配置文件,进行以下改动,把network_class_name改成dynamic_network_architectures.architectures.caunet.CAPlainConvUNet,如下图:
三、模型训练
完成了模型和数据集配置文件的修改后,开始训练模型,使用的数据集还是Task04_Hippocampus,以上的代码支持2d和3d模型,可以使用以下的训练命令:
nnUNetv2_train 4 2d 0
nnUNetv2_train 4 2d 1
nnUNetv2_train 4 2d 2
nnUNetv2_train 4 2d 3
nnUNetv2_train 4 2d 4
nnUNetv2_train 4 3d_fullres 0
nnUNetv2_train 4 3d_fullres 1
nnUNetv2_train 4 3d_fullres 2
nnUNetv2_train 4 3d_fullres 3
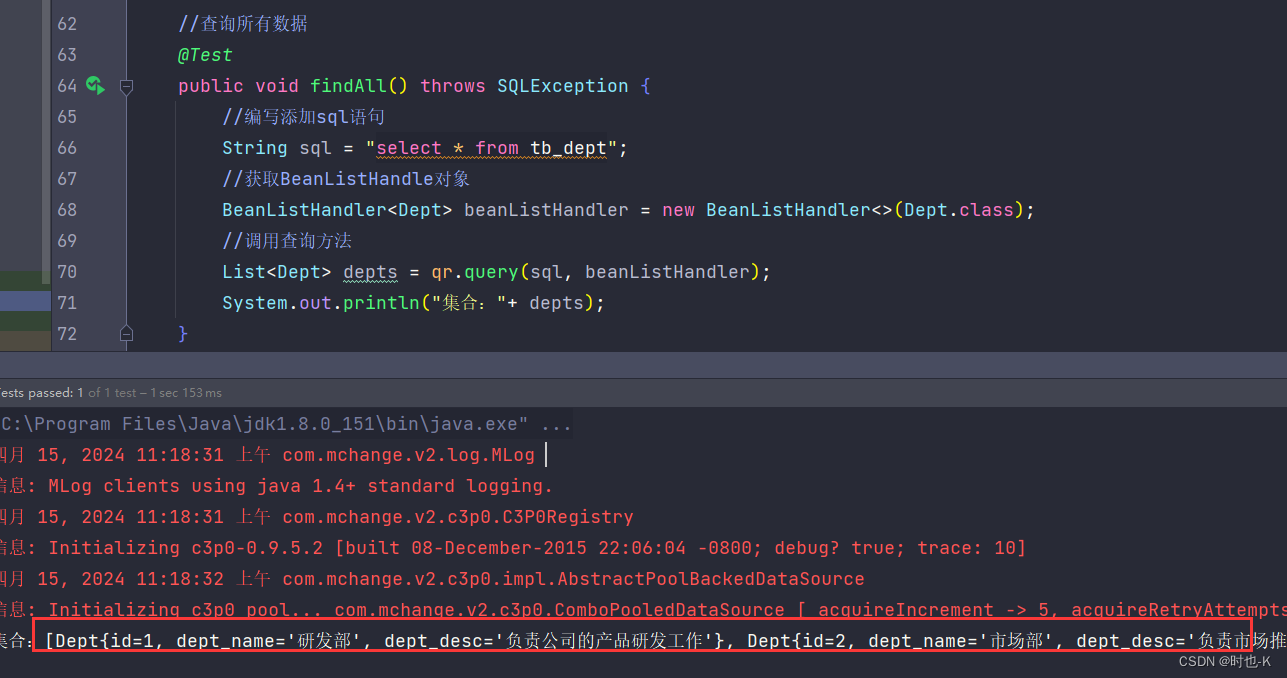
nnUNetv2_train 4 3d_fullres 4 可以看到模型已经成功跑起来了:

因为nnunet训练非常的久,实验资源有限,没有完成全部训练,只完成了代码修改及跑通。